Introduction to Construction Safety Training
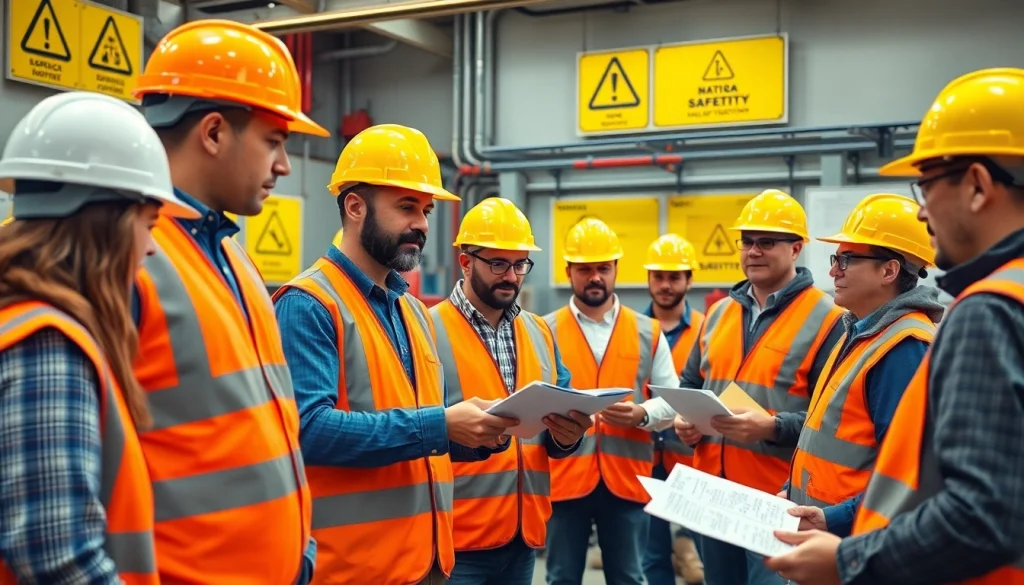
The construction industry is known for its numerous hazards and risks, making safety a top priority at worksites. Enhancing safety through effective training initiatives is essential for protecting workers, ensuring compliance with laws, and minimizing accidents. For organizations aiming to improve their safety protocols, construction safety training serves as a critical foundation for developing a culture of safety and accountability. This article will explore the significance of safety in construction, outline training objectives, and delve into regulatory requirements that shape these training programs.
Importance of Safety in Construction
Construction sites are often rife with potential dangers, including falls, equipment injuries, electrical hazards, and exposure to harmful substances. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), construction has one of the highest rates of work-related injuries and fatalities. Prioritizing safety does not only protect employees but also contributes to overall productivity, lowers insurance costs, and enhances the company’s reputation. When workers feel safe and valued, their morale improves, leading to increased job satisfaction and retention. Thus, prioritizing construction safety translates into financial and operational benefits for organizations.
Overview of Training Objectives
Effective construction safety training aims to achieve several key objectives. First, it seeks to raise awareness about the common hazards present on construction sites. Second, it provides workers with essential information and knowledge about the appropriate safety protocols to follow. Third, training fosters a sense of responsibility among employees to prioritize safety for themselves and their colleagues. Lastly, by encouraging active participation in safety procedures, training aims to embed safety practices into the culture of the organization. Ultimately, these objectives combine to reduce the risk of accidents and create safer workplaces.
Understanding Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory requirements for safety training vary by region and are influenced by industry standards. Organizations must adhere to OSHA guidelines, which stipulate that employers provide a safe working environment, including community outreach programs, safety training, and personal protective equipment (PPE). Awareness of these regulations not only ensures compliance but also guides the development of training programs that align with best safety practices. Understanding these regulations also aids in mitigating legal risks and improving the organization’s standing in the industry.
Key Components of Effective Construction Safety Training
Curriculum Development and Materials
The development of an effective safety training curriculum is a fundamental component that requires a thorough understanding of the specific hazards faced by employees in their particular job roles. Training materials should be comprehensive, incorporating the latest industry standards and best practices. A combination of instructional methods, including lectures, hands-on training, and interactive sessions can enhance learning outcomes. Moreover, incorporating visuals like diagrams and videos can cater to different learning styles and make the information more accessible. It’s crucial to regularly update training materials to reflect changes in regulations or project scopes.
Engaging Training Delivery Methods
To maximize the effectiveness of construction safety training, delivering the content in engaging ways is essential. Traditional lecturing may not be sufficient to maintain the attention of workers. Innovative approaches like simulation training, role-playing scenarios, and case studies can enhance learning engagement. These methods allow workers to practice real-life situations, fostering critical thinking and decision-making skills vital to navigating hazards. Additionally, utilizing technology, such as virtual reality or e-learning modules, can provide flexible learning options, making it easier for workers to complete their training at their convenience.
Assessing Prior Knowledge and Skills
Understanding the existing knowledge and skills of workers is crucial for tailoring construction safety training programs. Conducting pre-training assessments can identify gaps in knowledge and highlight areas requiring focus. Techniques such as surveys, quizzes, or informal interviews can provide insight into the current safety practices and attitudes of employees. By assessing prior knowledge, organizations can design training sessions that are relevant and targeted. Continuous evaluation post-training can further ensure that the workforce adequately retains the safety protocols necessary for their roles.
Challenges and Solutions in Construction Safety Training
Addressing Workforce Diversity
Construction sites often feature diverse workforces, including varying age groups, cultural backgrounds, and levels of experience. This diversity can present challenges in delivering effective safety training that resonates with all workers. To address these challenges, training programs should be inclusive and culturally sensitive. Incorporating multilingual materials and recognizing varying literacy levels can help ensure that all employees comprehend safety protocols. Moreover, creating an environment of open dialogue encourages workers to voice concerns or ask questions, enhancing overall safety comprehension.
Overcoming Resistance to Training
Resistance to safety training can stem from various factors, including perceived irrelevance or time constraints. Workers may view training as an interruption to their daily tasks rather than a necessary investment in their safety. Addressing these concerns involves demonstrating the tangible benefits of safety training, such as reducing the likelihood of injuries, which can ultimately save time and resources. Moreover, management should lead by example and clarify the importance of safety by actively participating in safety training sessions and prioritizing worker health and safety as core organizational values.
Ensuring Retention of Safety Practices
Ensuring that workers retain knowledge from safety training is another significant challenge. Short-term retention rates often decrease over time, leading to safety complacency. To combat this, organizations should implement follow-up training or refresher courses regularly. Additionally, promoting ongoing safety discussions at team meetings and using tools such as safety bulletins or newsletters can reinforce safety practices. Creating a rewards system for safe practices can also motivate employees to actively engage in maintaining a safe working environment.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Construction Safety Training
Evaluation Techniques and Feedback
Measuring the effectiveness of construction safety training is essential for ensuring that it meets its objectives. Evaluating training programs can be accomplished through various techniques, including surveys, observation, and performance metrics. Gathering feedback from participants about the training sessions helps identify strengths and areas for improvement. Management should consider establishing a continuous feedback loop, allowing workers to express their opinions on the training content and delivery. This feedback can lead to necessary adjustments, enhancing future training initiatives.
Performance Metrics to Monitor
To accurately assess the impact of safety training, organizations should establish performance metrics that highlight key indicators of success. Metrics may include the number of workplace incidents and accidents, near-miss reporting, employee turnover rates, and the results of follow-up knowledge assessments. Regularly tracking these metrics will provide a clearer picture of safety training effectiveness and highlight areas requiring attention. Incorporating these metrics into a broader safety performance dashboard can also aid in visualizing progress and facilitating strategic planning.
Continuous Improvement Strategies
Continuous improvement is essential in maintaining an effective construction safety training program. Regular reviews of training content and delivery methods should align with the evolving landscape of construction safety regulations. Organizations should stay informed about new safety technologies and best practices that can improve training effectiveness. Incorporating lessons learned from incidents or near misses can also refine training approaches. Establishing a culture of continuous improvement encourages all staff to contribute to safety enhancements, resulting in a proactive rather than reactive safety culture.
Best Practices for Implementing Construction Safety Training
Creating a Safety Culture in the Workplace
Establishing a strong safety culture within the organization is vital for successful construction safety training implementation. Management should demonstrate a commitment to safety through their actions and decision-making. Involving employees in safety committees or assigning safety ambassadors can foster ownership of safety practices among workers. Regularly discussing safety in team meetings and acknowledging safe practices and employees demonstrate that safety is a priority. This ingrained culture of safety becomes an integral part of the organization’s identity, influencing behaviors and decisions at all levels.
Leveraging Technology for Training Enhancement
Advancements in technology present numerous opportunities to enhance construction safety training. From virtual simulations to mobile training applications, technology can facilitate more engaging and flexible training experiences. E-learning platforms enable organizations to offer training that employees can access anytime, anywhere, making it easier to accommodate various schedules. Additionally, data analytics can track training completion rates, identify knowledge gaps, and provide insights for continuous improvement. Integrating technology into safety training not only modernizes the approach but also aligns with the expectations of a younger, tech-savvy workforce.
Tips for Ongoing Engagement and Learning
Ongoing engagement in safety practices is crucial for long-term retention of skills and knowledge. Organizations can enhance engagement by incorporating safety into the daily routine, such as conducting daily safety check-ins or toolbox talks. Encouraging peer-to-peer learning through mentorship programs can further reinforce knowledge sharing. Additionally, integrating gamification elements into training, such as safety challenges or competitions, can make learning fun and motivate team participation. By fostering an environment of continuous learning, organizations can ensure that safety remains at the forefront of the workplace culture.