Understanding Structural Steel Installation
Definition and Importance of Structural Steel Installation
Structural steel installation is a critical component in the construction and engineering industries. It involves the assembly of steel frameworks that serve as the building blocks for various structures, including commercial buildings, bridges, and industrial facilities. This form of installation plays a vital role in ensuring the safety, durability, and integrity of any structure. Steel’s ability to withstand extreme loads and stresses makes it an ideal choice for modern construction, where both aesthetics and functionality are key.
Applications in Various Industries
Structural steel finds applications across multiple industries. In the construction sector, it enables the erection of skyscrapers and large warehouses due to its high strength-to-weight ratio. The automotive industry relies on steel for manufacturing frames and body structures, while the energy sector utilizes it for wind turbines and oil platforms. Additionally, transportation infrastructure, such as bridges, uses structural steel to support heavy vehicular loads. Each of these applications illustrates the versatility and essential nature of structural steel installation in contemporary society.
Components of Structural Steel Systems
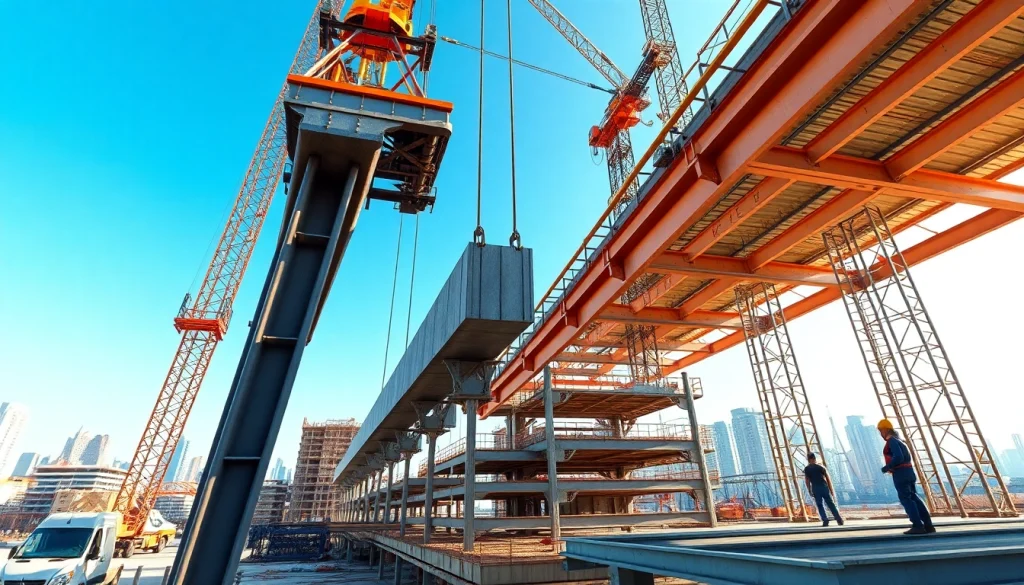
Understanding the components of structural steel systems is key for effective installation. Major components include beams, columns, girders, trusses, and connectors. Beams are horizontal members that bear loads from above, while columns support vertical loads. Girders act as main horizontal supports, often connecting beams. Trusses are engineered frameworks designed to provide inherent strength with minimal weight, while connectors like bolts and welds are crucial for joining different structural elements securely. Together, these components create a robust structure that can sustain various forces from its environment.
Planning for Structural Steel Installation
Essential Pre-Installation Considerations
Effective planning for structural steel installation begins long before the actual installation takes place. Pre-installation considerations include compliance with building codes and regulations, material procurement, and determining the timeline for construction. It’s essential to engage structural engineers and architects early in the process to identify the design specifications and allowable load capacities. Budgeting accurately ensures that costs are managed and resources are optimized throughout the project.
Site Assessment and Preparation Steps
A thorough site assessment lays the foundation for a successful structural steel installation. This assessment involves evaluating soil conditions, existing utilities, and access for construction vehicles. Proper preparation includes clearing the site, grading land, and establishing a safe work environment. Ensuring that the site is level and ready for the steel components not only streamlines the installation process but also mitigates risks that could lead to structural failures later on.
Creating an Effective Installation Plan
An effective installation plan encompasses logistical considerations, workforce management, and timelines. Identifying the order of installation is crucial; typically, columns are erected first, followed by beams and other elements. This phase also includes contingency plans for potential weather delays and equipment malfunctions. Coordinating communication among team members ensures that everyone is aligned on the plan, enhancing the overall efficiency and safety of the installation process.
Key Techniques for Structural Steel Installation
Methods of Erecting Steel Structures
There are several methods for erecting structural steel, including conventional cranes, modular construction, and use of advanced technologies like robotics. Traditional crane methods are commonly employed due to their flexibility and ability to place heavy steel components accurately. Modular construction, on the other hand, allows for sections of a building to be prefabricated off-site and then assembled on-site, significantly reducing construction time and labor costs. Advanced technologies like drones for site surveying and robotic arms for precise assembly are becoming increasingly popular.
Advantages of Advanced Installation Techniques
Utilizing advanced installation techniques can lead to numerous advantages. For instance, modular construction often results in lower overall project costs and reduced waste due to efficient material use. Furthermore, employing technologies like Building Information Modeling (BIM) allows for enhanced visualization and coordination throughout the project, minimizing misunderstandings and errors during the installation phase. These innovations not only speed up the process but also improve the quality of the end result.
Safety Protocols During Installation
Safety is paramount during structural steel installation. Following established safety protocols helps protect workers from accidents and hazards. Essential safety practices include regular safety training, proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and thorough inspections of equipment prior to use. Implementing fall protection systems, including guard rails and harnesses, is also crucial, particularly when working at heights. Ensuring that all workers are familiar with safety protocols fosters a culture of safety on the job site.
Common Challenges in Structural Steel Installation
Identifying Frequent Obstacles
Despite careful planning, various challenges may arise during structural steel installation. Common obstacles include unforeseen weather conditions that can delay progress, miscalculations in material requirements leading to shortages, and communication breakdowns among team members. Additionally, navigating site-specific challenges such as existing infrastructure or limited space poses significant hurdles that must be addressed effectively to keep projects on track.
Strategies to Overcome Installation Issues
Overcoming installation challenges requires proactive problem-solving strategies. For example, conducting regular progress meetings can help ensure that all team members are informed of changes or delays that may impact the timeline. Establishing relationships with reliable material suppliers can minimize the risk of shortages, while flexible scheduling can accommodate unexpected weather conditions. Incorporating technology that provides real-time updates can also improve communication and streamline workflows.
Case Studies of Successful Problem Solving
Analyzing case studies of successful projects provides valuable insights into effective problem-solving during structural steel installation. One notable case involved a large-scale project where mid-installation assessments identified a flaw in the design due to overlooked specified loads. By swiftly engaging design engineers and iteratively refining the approach, the team was able to implement a revised design that not only met the original specifications but also improved overall stability against environmental stresses. These experiences highlight the importance of adaptability in installation efforts.
Measuring Success in Structural Steel Installation
Performance Metrics to Consider
To assess the success of a structural steel installation project, key performance metrics must be established. These can include project timelines, budget adherence, safety incident rates, and overall structural integrity assessments post-installation. Tracking these metrics allows construction managers to determine the effectiveness of their strategies and make informed adjustments for future projects. Additionally, engaging stakeholders in reviewing these metrics can deepen their understanding of project successes and areas for improvement.
Quality Control in Structural Steel Projects
Quality control is crucial in structural steel installation to ensure that the final product meets all design and safety requirements. This entails rigorous inspection processes during and after each phase of installation. Implementing non-destructive testing methods can identify defects without compromising structural integrity. Regular audits and quality assurance checks throughout the installation process help ensure compliance with relevant codes and standards, thereby safeguarding the overall quality of the project.
Feedback Loops and Continuous Improvement
Establishing feedback loops involves gathering input from all stakeholders, including project managers, construction workers, and clients. This feedback can highlight strengths and weaknesses of the installation process, providing insights for continuous improvement. Following the completion of a project, conducting debrief meetings to discuss what worked well and what could be enhanced contributes to building a more resilient and efficient installation framework for future projects. Adopting a mindset of continuous improvement ultimately elevates the quality and effectiveness of structural steel installation in every project.