Understanding Mould Temperature Controllers
The manufacturing industry has witnessed remarkable advancements in technology over the past few decades, with a strong focus on optimizing processes to enhance productivity and product quality. One critical component in this evolution is the Mould Temperature Controller, which plays a vital role in determining the quality of molded products. By maintaining optimal temperatures during the molding process, manufacturers can significantly reduce defects and improve overall output. This comprehensive guide explores the importance, functionality, and latest innovations in mould temperature controllers, particularly the fourth-generation systems revolutionizing industrial manufacturing.
What is a Mould Temperature Controller?
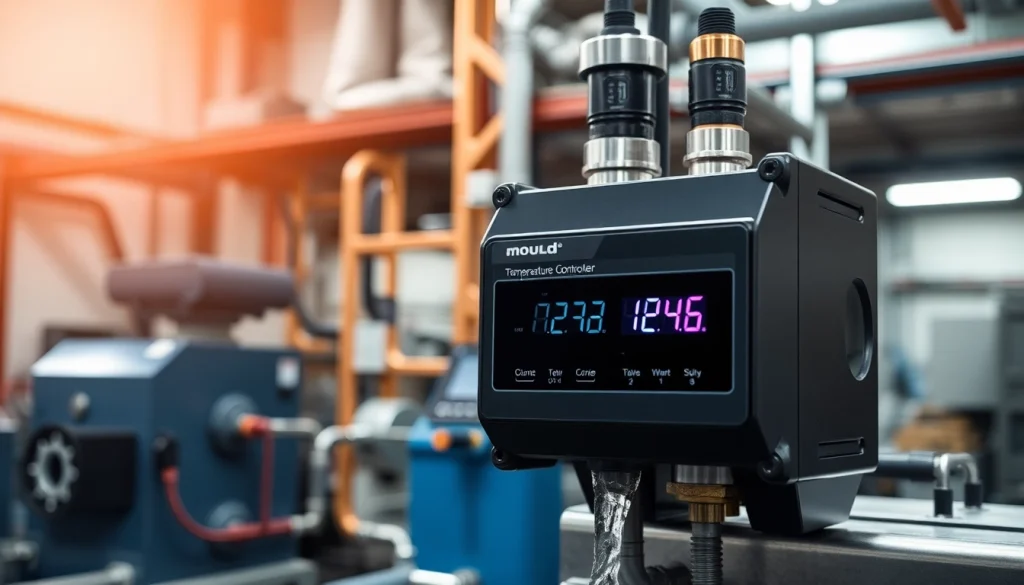
A mould temperature controller is a specialized device designed to regulate and maintain the temperature of a mold during the manufacturing process, particularly in injection molding. By ensuring that the mould reaches and maintains a specified temperature, these controllers help in achieving consistent product quality, minimizing production defects, and enhancing overall operational efficiency. Typically, these systems utilize various fluid mediums, such as water or oil, to transfer heat to or from the mould, depending on the requirements of the process.
The Importance of Temperature Control in Manufacturing
Effective temperature management is critical in manufacturing, particularly in processes such as injection molding, where the flow and cooling of molten material directly affect the finished product’s quality. Insufficient heating or cooling can lead to:
- Defects: Inconsistent tempering can result in warping, shrinkage, or surface imperfections, ultimately leading to higher rejection rates.
- Increased Cycle Times: Poor temperature control can extend production cycles, causing delays and increased costs.
- Material Wastage: Inefficient temperature management leads to higher energy consumption and waste of raw materials due to rejects.
Hence, integrating advanced mould temperature controllers into the manufacturing process is essential for achieving optimal results and maintaining competitiveness in the market.
Key Features of Advanced Mould Temperature Controllers
Modern mould temperature controllers come equipped with several advanced features designed to enhance efficiency and precision in temperature management:
- Intelligent Control Systems: These systems employ advanced algorithms, such as PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) control, to ensure accurate and stable temperature regulation.
- Rapid Cooling and Heating: Enhanced designs allow for quicker temperature adjustments, reducing cycle times significantly.
- Durability and Maintenance: High-quality materials and robust construction minimize downtime due to maintenance, thus optimizing productivity.
How the Fourth-Generation Controller Stands Out
The fourth-generation mould temperature controller has emerged as a game-changer in the industry, bringing a host of innovations that significantly improve efficiency and reliability in mold management.
Innovative Cooling Techniques for Faster Mold Change
One of the standout features of this generation of mould temperature controllers is their forced cooling capability. Traditional methods often require long cooling periods, where moulds must cool down completely before being replaced—this can take hours. However, with the fourth-generation system, mold temperatures can be reduced in as little as 10 minutes through forced cooling techniques. For instance, the controller continuously opens the cooling solenoid valve, facilitating rapid cooling and allowing for faster mold changes. By preheating the mould one hour in advance, manufacturers can achieve a 10% increase in efficiency, dramatically reducing transition times during production.
Precision Control: The Role of PID Algorithms
The precision of the fourth-generation mould temperature controller is significantly enhanced through the use of the latest PID temperature control algorithms. These algorithms not only increase temperature control efficiency by 10% but also ensure high-temperature uniformity across the mold. Such precision (±0.1℃) translates directly into improved product yields, as a consistent temperature minimizes defects during the molding process. Additionally, solid-state relays employed in the hardware enable a rapid response time of 0.1 seconds, ensuring that temperature fluctuations are kept within acceptable limits.
Durability and Maintenance: Materials Matter
Mould temperature controllers must withstand harsh industrial conditions, which makes the choice of materials crucial. The fourth-generation systems utilize upgraded copper heaters that significantly enhance durability by minimizing the adherence of impurities and scaling, thanks to copper’s excellent ductility and thermal conductivity. This not only extends the lifespan of the heater (by 40%) but also ensures optimal efficiency. Furthermore, these controllers are designed to handle poor-quality water, equipped with a 50-mesh high-precision filter or an optional 30μm filtration-grade filter, effectively preventing clogging and ensuring smooth operations.
Benefits of Implementing a Mould Temperature Controller
Investing in a high-quality mould temperature controller brings numerous advantages that can transform a manufacturing process.
Reducing Production Time and Increasing Output
By enabling faster mold changes and effective temperature management, these controllers play a critical role in reducing overall production times. For example, if a manufacturing facility can reduce mold change times from hours to mere minutes, this can significantly increase the total output per day—resulting in greater profits and a better return on investment.
Improving Product Quality and Yield Rates
Quality is non-negotiable in manufacturing. By ensuring stable and optimal temperatures throughout the molding process, the fourth-generation mould temperature controller minimizes product defects, leading to higher yield rates. This consistency enhances customer satisfaction and reduces the costs associated with rework or scrap.
Cost-Effectiveness in Long-Term Operations
Though the initial investment in advanced temperature control technology may be significant, the long-term savings are compelling. Reduced waste, improved efficiency, and enhanced product quality all contribute to a favorable cost-benefit ratio. Over time, the savings from decreased energy consumption and fewer production disruptions can offset the initial expenses, making it a sound investment.
Challenges in Mould Temperature Management
While modern mould temperature controllers provide numerous advantages, there are still challenges within the domain of temperature management that manufacturers must address.
Common Misconceptions About Temperature Control
Many decision-makers mistakenly believe that temperature control is a one-time setup rather than an ongoing process. In reality, it requires continual monitoring and adjustments to maintain optimal conditions, especially when dealing with varying production materials or environmental factors. Emphasizing an ongoing approach to temperature management can lead to better overall outcomes.
Dealing with Poor Water Quality: Solutions Available
Water quality significantly impacts the performance of mould temperature controllers. Poor water conditions can lead to scaling and corrosion, negatively affecting the efficiency and longevity of the system. However, advanced filtration systems, like those used in the fourth-generation controllers, help mitigate these issues by effectively filtering out impurities. Additionally, using pure water in a closed circulation system minimizes the risk of corrosion and scaling, ensuring that the mould remains in optimal condition.
Technological Limitations and Opportunities
Despite the advancements in mould temperature controllers, challenges remain concerning integration with older machinery and system compatibility. Innovations in connectivity, such as IoT capabilities, provide an opportunity to enhance system efficiency through data analysis, predictive maintenance, and performance monitoring. Manufacturers willing to embrace these technologies can remain competitive in an evolving market.
Future Trends in Mould Temperature Control Technologies
The future of mould temperature control technologies looks promising, with several emerging trends poised to change the landscape of industrial manufacturing.
Emerging Technologies for Enhanced Efficiency in 2025
As the manufacturing landscape becomes increasingly digitized, machine learning and AI-driven solutions will play a crucial role in mould temperature management. Predictive algorithms can analyze historical data to optimize temperature settings, reduce energy consumption, and enhance system responsiveness. These technologies will allow manufacturers to become more proactive in managing their production processes.
Sustainability in Temperature Control Systems
With growing concerns over environmental impact, sustainable practices are becoming paramount in manufacturing. Future mould temperature controllers will likely incorporate energy-efficient designs and materials. Implementing systems that minimize energy use while maintaining optimal performance will not only help manufacturers comply with regulations but also appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Industry Insights: What to Expect Moving Forward
As we approach 2025, the trend towards automation and integration of advanced sensors in mould temperature controllers will continue to gain momentum. Manufacturers will need to be prepared for these changes by investing in systems that can adapt to new technologies and market demands. The emphasis will increasingly be on achieving a balance between efficiency, quality, and sustainability in operations.